- HOME/
- About Stanley/
- Stanley's 100th Anniversary Site
Stanley's 100th Anniversary Site

The Rebuilding of Management Foundation
Masahiro Shinoda, who became the President in 1990, considered as an emergency the significant drop in the company's profits experienced in the previous year for the first time since its formation. He therefore initiated efforts to establish a solid management foundation under a new structure. His expression of the new ideal corporate structure for the 21st century was "a good company." In order to rebuild its management foundation, the planning function of the company was strengthened with new systems such as Chain System (a profit management system), Stars Plan (a new personnel system), and DN-6 (an information system). In addition, the company started "SNAP," activities for production innovations, by establishing the basic principles of manufacturing and how to implement them. From 1990 to 1999, it was the decade in which the company's management foundation, infrastructure, and systems for the years from 2000 to present day were built under the initiative of then-Vice President Takanori Kitano, who was later appointed as the President.
Download the Chapter 5 PDFCHRONOLOGY
Appointed then-Senior Managing Director Masahiro Shinoda as President and then-Managing Director Takanori Kitano Senior Managing Director
Capital stock exceeded 20 billion JPY
Introduced matrix management system emphasizing corporate-wide management functions
Certified as No. 1 for quality in the field of subminiature lamps by U.S. Ford
THS listed on the Stock Exchange of Thailand
The Start of the DN-6, an Information System Development 6-year Plan
In February 1988, Stanley Electric reorganized its then-existing computer system office into the Dia Net Center to streamline business processes such as sales, engineering, purchasing, production, and accounting, and then started an information system development 6-year plan (DN-6) to develop a comprehensive information system to enable the company to identify and solve problems at an enhanced speed. After reviewing the product codes necessary for systematization, the company developed information system infrastructures to implement centralized information management based on networks and databases in stages, beginning with the launch of the production management system Phoenix in June 1989. Starting from 1996, DN-6 was replaced with Dia Net Plans '96, '97, and '98. The company made efforts to equip itself with global and more advanced information technologies for the 21st century, including the utilization of groupware and the development of intranets. These efforts led to the company's ERPs and new cost control system currently being in operation.
Launched a new personnel system (Stars Plan), implementing a new evaluation system and challenge target system
Research and Development Corporation (currently Japan Science and Technology Agency) certified the successful development of the manufacturing technology of CSH-LCD
Opened the Yokohama Technical Center (YTC)
Launched multi-reflector fog lamp, RAYBRIG R011
The Introduction of Stars Plan (New Personnel System)
In April 1991, Stanley Electric introduced long-term competency-based personnel measures in order to "establish a corporate culture in which people who were aspiring and willing to learn can be respected."
In the 1990s, many enterprises were shifting toward a results-based system in pursuit of better results and figures. In a results-based system, however, a pay raise and rewards are hard to come by without better results, and focus tended to be on short-term gain rather than long-term growth. Then-Representative Senior Managing Director Takanori Kitano, who was leading the introduction of the Stars Plan, thought that people could not be motivated solely with a profit-centered corporate mindset. He was convinced that people were less motivated by a profit-based system and more by personal feelings. Although a results-based system was important, a singular focus on results would lead to management with an excessively short-term perspective.
He therefore thought that the effective use of human resources should be a higher priority and placed emphasis on nurturing people (competency-based system). This involved the idea that an organization would change if its people changed and that a company could contribute to society if its organizations were vibrant.
He further hoped that this personnel management policy would change everyone's consciousness. More specifically, he wanted each individual to recognize that working with passion, interest, and responsibility for his or her growth would lead to the happiness of everyone, the company, and society.
The Stars Plan was a reflection of these thoughts on management system. Under this system, evaluation processes were made visible to ensure impartial, reasonable, and valid evaluations were conducted by two categories: competency and performance. Further, employees received direct feedback on their evaluation results. Also, new qualification and wage systems based on a competency-based system were introduced. The Stars Plan was also gradually introduced to overseas affiliated companies.
Launched blue LEDs
Automotive multi-lamp "Jabalina" awarded Good Design product in October 1992
LED display board at Narita International Airport
Established Stanley Electric (H.K.) Co., Ltd. (SHK)
Launched ultrathin, high-brightness chip type LEDs
Launched RAYBRIG Hyper Halogen, the world's first high efficiency bulb
Acquired shares of Matsuo Electric Co., Ltd. and made it a special subsidiary for the purpose of employing disabled people
Expanded into new EL business
Stanley Finance and Service Co., Ltd. restarted as Stanley Pal Co., Ltd.
Yamagata Factory (exclusive manufacturing of LED chips) started full operations
Stars Plan shifted to Ver. 2 (introduced new qualification acquisition policies and a new wage system)
Launched Active 30
Capital participation in LUMAX of India
Strobes on the DC-1, RICOH's first digital camera
Established the basic principles of production control
Established Stanley Electric Shayukai (Association of Retirees)
Implemented union shop system
Established Tianjin Stanley Electric Co., Ltd. in China
Implemented job change support system
First domestic High Intensity Discharge (HID) headlamps were approved
Established the Active 30 Promotion Office
HID lamps on the Mitsubishi Motors Super Great, the first time in Japan for mass produced vehicles
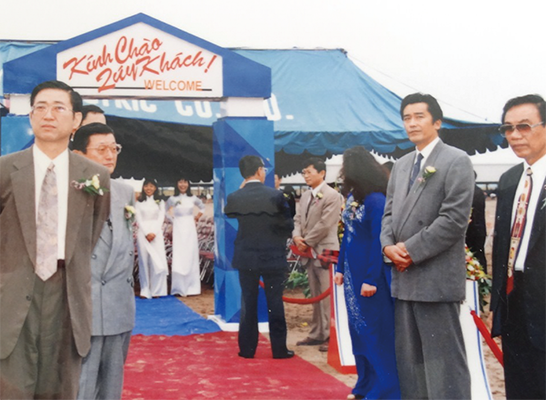
Established Vietnam Stanley Electric Co., Ltd. (VNS)
Established Shanghai Stanley Electric Co., Ltd. (SSE)
First training session by Hitoshi Yamada of PEC Productivity Education Center (currently PEC Kyokai (PEC Institution))
Renamed Active 30 Promotion Office as SNAP Promotion Office
Published The Stanley Way: 75 Years of Stanley Electric
Renamed SHK as Stanly Electric (Asia Pacific) Ltd. (SAP)
Announced HRM230S as a new module for infrared communication modules compliant with IrDA 1.1 (4 Mbps)
SNAP Production Innovation Activity
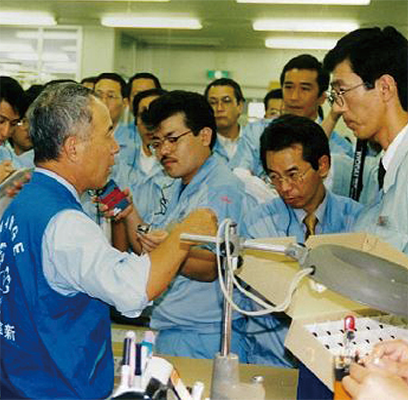
In September 1994, Stanley Electric started Active 30 to improve cost competitiveness by 30%. Active 30 was designed to improve productivity by eliminating waste, reducing costs, developing new markets, proposing development plans to gain a leading edge, and reducing lead time to increase profit levels,. Active 30 was an initiative to improve cost competitiveness mainly through the streamlining and rationalization in administrative and non-production departments. Meanwhile, SNAP (Stanley New Approach for Higher Productivity) was an initiative started in 1995 to streamline and rationalize production processes. Then in May 1997, the company started to receive guidance from the PEC Industrial Education Center, which had a long experience in introducing Toyota Production System to many firms. The guidance helped the company steadily achieve better results.
Established Stanley Electric Sales of America, Inc. (SSA)
Capital participation in Samlip Lighting Corporation of South Korea
Decided to centralize and reorganize the LCD business
Established Stanley Electric GmbH (SED)
Renamed Hatano Denko K.K. as STANLEY WELL Corporation and made it a special subsidiary for the purpose of employing disabled people
Internally and externally announced Environmental Declaration as part of environmental conservation activities
Stanley Suburban Office Surf-side completed
Launched high-brightness chip type LED with lens
Announced ultrathin headlamp, Line Beam, at the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) International Conference & Exhibition '99
Appointed then-Senior Managing Director Masahiro Shinoda as President and then-Managing Director Takanori Kitano Senior Managing Director

Senior Managing Director Takanori Kitano explaining about the establishment of the three systems of Profit Control, Human Resources and Information
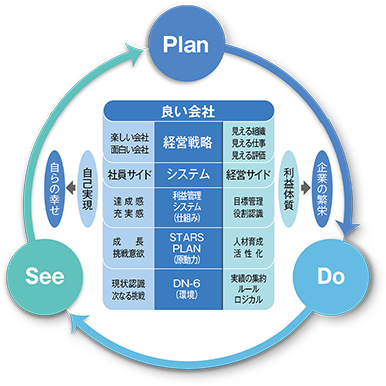
Business activities in P-D-S cycle
Capital stock exceeded 20 billion JPY
Introduced matrix management system emphasizing corporate-wide management functions
Certified as No. 1 for quality in the field of subminiature lamps by U.S. Ford
THS listed on the Stock Exchange of Thailand
The Start of the DN-6, an Information System Development 6-year Plan
In February 1988, Stanley Electric reorganized its then-existing computer system office into the Dia Net Center to streamline business processes such as sales, engineering, purchasing, production, and accounting, and then started an information system development 6-year plan (DN-6) to develop a comprehensive information system to enable the company to identify and solve problems at an enhanced speed. After reviewing the product codes necessary for systematization, the company developed information system infrastructures to implement centralized information management based on networks and databases in stages, beginning with the launch of the production management system Phoenix in June 1989. Starting from 1996, DN-6 was replaced with Dia Net Plans '96, '97, and '98. The company made efforts to equip itself with global and more advanced information technologies for the 21st century, including the utilization of groupware and the development of intranets. These efforts led to the company's ERPs and new cost control system currently being in operation.
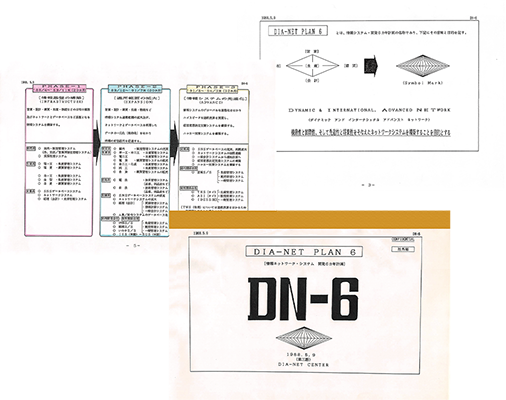
Proposal of the DN-6, an information system development 6-year plan
Launched a new personnel system (Stars Plan), implementing a new evaluation system and challenge target system
The Introduction of Stars Plan (New Personnel System)
In April 1991, Stanley Electric introduced long-term competency-based personnel measures in order to "establish a corporate culture in which people who were aspiring and willing to learn can be respected."
In the 1990s, many enterprises were shifting toward a results-based system in pursuit of better results and figures. In a results-based system, however, a pay raise and rewards are hard to come by without better results, and focus tended to be on short-term gain rather than long-term growth. Then-Representative Senior Managing Director Takanori Kitano, who was leading the introduction of the Stars Plan, thought that people could not be motivated solely with a profit-centered corporate mindset. He was convinced that people were less motivated by a profit-based system and more by personal feelings. Although a results-based system was important, a singular focus on results would lead to management with an excessively short-term perspective.
He therefore thought that the effective use of human resources should be a higher priority and placed emphasis on nurturing people (competency-based system). This involved the idea that an organization would change if its people changed and that a company could contribute to society if its organizations were vibrant.
He further hoped that this personnel management policy would change everyone's consciousness. More specifically, he wanted each individual to recognize that working with passion, interest, and responsibility for his or her growth would lead to the happiness of everyone, the company, and society.
The Stars Plan was a reflection of these thoughts on management system. Under this system, evaluation processes were made visible to ensure impartial, reasonable, and valid evaluations were conducted by two categories: competency and performance. Further, employees received direct feedback on their evaluation results. Also, new qualification and wage systems based on a competency-based system were introduced. The Stars Plan was also gradually introduced to overseas affiliated companies.
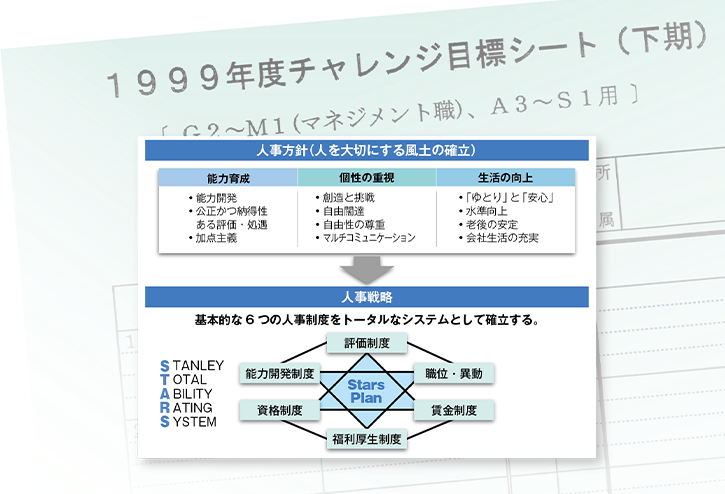
STARS Plan
Research and Development Corporation (currently Japan Science and Technology Agency) certified the successful development of the manufacturing technology of CSH-LCD
Opened the Yokohama Technical Center (YTC)
Launched multi-reflector fog lamp, RAYBRIG R011
Launched blue LEDs
Automotive multi-lamp "Jabalina" awarded Good Design product in October 1992
LED display board at Narita International Airport
Established Stanley Electric (H.K.) Co., Ltd. (SHK)
Launched ultrathin, high-brightness chip type LEDs
Launched RAYBRIG Hyper Halogen, the world's first high efficiency bulb
Acquired shares of Matsuo Electric Co., Ltd. and made it a special subsidiary for the purpose of employing disabled people
Expanded into new EL business
Stanley Finance and Service Co., Ltd. restarted as Stanley Pal Co., Ltd.
Yamagata Factory (exclusive manufacturing of LED chips) started full operations
Stars Plan shifted to Ver. 2 (introduced new qualification acquisition policies and a new wage system)
Launched Active 30
SNAP Production Innovation Activity
In September 1994, Stanley Electric started Active 30 to improve cost competitiveness by 30%. Active 30 was designed to improve productivity by eliminating waste, reducing costs, developing new markets, proposing development plans to gain a leading edge, and reducing lead time to increase profit levels,. Active 30 was an initiative to improve cost competitiveness mainly through the streamlining and rationalization in administrative and non-production departments. Meanwhile, SNAP (Stanley New Approach for Higher Productivity) was an initiative started in 1995 to streamline and rationalize production processes. Then in May 1997, the company started to receive guidance from the PEC Industrial Education Center, which had a long experience in introducing Toyota Production System to many firms. The guidance helped the company steadily achieve better results.
Capital participation in LUMAX of India
Strobes on the DC-1, RICOH's first digital camera
Established the basic principles of production control
Established Stanley Electric Shayukai (Association of Retirees)
Implemented union shop system
Established Tianjin Stanley Electric Co., Ltd. in China
Implemented job change support system
First domestic High Intensity Discharge (HID) headlamps were approved
Established the Active 30 Promotion Office
HID lamps on the Mitsubishi Motors Super Great, the first time in Japan for mass produced vehicles
Established Vietnam Stanley Electric Co., Ltd. (VNS)
Established Shanghai Stanley Electric Co., Ltd. (SSE)
First training session by Hitoshi Yamada of PEC Productivity Education Center (currently PEC Kyokai (PEC Institution))
Renamed Active 30 Promotion Office as SNAP Promotion Office
Published The Stanley Way: 75 Years of Stanley Electric
Renamed SHK as Stanly Electric (Asia Pacific) Ltd. (SAP)
Announced HRM230S as a new module for infrared communication modules compliant with IrDA 1.1 (4 Mbps)
Established Stanley Electric Sales of America, Inc. (SSA)
Capital participation in Samlip Lighting Corporation of South Korea
Decided to centralize and reorganize the LCD business
Established Stanley Electric GmbH (SED)
Renamed Hatano Denko K.K. as STANLEY WELL Corporation and made it a special subsidiary for the purpose of employing disabled people
Internally and externally announced Environmental Declaration as part of environmental conservation activities
Stanley Suburban Office Surf-side completed
Launched high-brightness chip type LED with lens
Announced ultrathin headlamp, Line Beam, at the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) International Conference & Exhibition '99